Gluten-Free Certification Steps
Understanding Gluten-Free Certification
Gluten-free certification is a process that ensures products meet strict standards for gluten content, typically less than 20 parts per million (ppm). This certification is crucial for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, as it provides confidence that the product is safe to consume. The certification process involves rigorous testing and compliance with specific guidelines set by certifying organizations.
Certification bodies, such as the Gluten-Free Certification Organization (GFCO) and the Celiac Support Association (CSA), play a pivotal role in this process. They evaluate products, ingredients, and manufacturing practices to ensure they adhere to gluten-free standards. Understanding the importance of certification helps consumers make informed choices and supports manufacturers in building trust with their audience.

Why Gluten-Free Certification Matters
For individuals with celiac disease, even trace amounts of gluten can trigger severe health issues. Gluten-free certification provides a layer of safety, ensuring that products are free from harmful levels of gluten. Beyond health concerns, certification also builds consumer trust. When a product carries a recognized gluten-free label, it signals transparency and commitment to quality.
For manufacturers, certification can open doors to a growing market of gluten-free consumers. It differentiates products in a competitive marketplace and demonstrates a dedication to inclusivity. Additionally, certification can reduce the risk of legal issues related to mislabeling or contamination, protecting both the brand and the consumer.

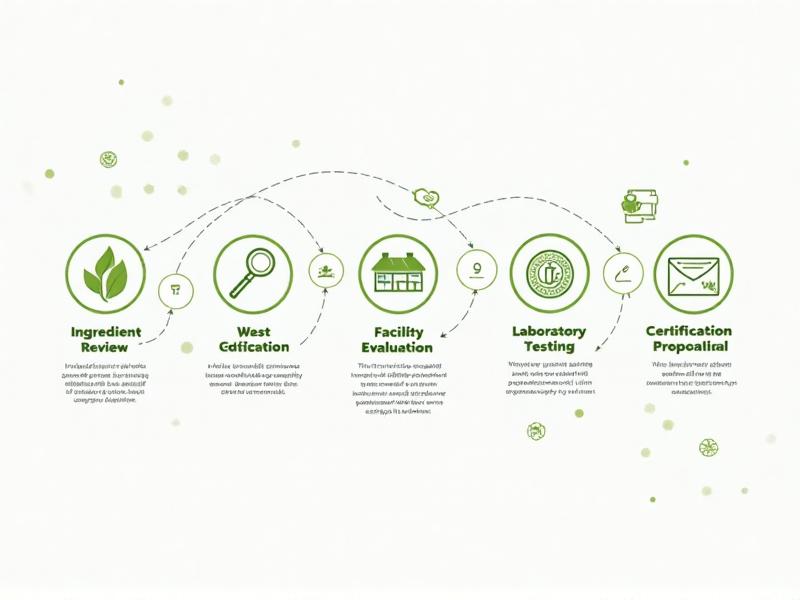
Steps to Obtain Gluten-Free Certification
The process of obtaining gluten-free certification begins with a thorough review of ingredients and manufacturing practices. Manufacturers must ensure that all components of their product meet gluten-free standards. This often involves sourcing ingredients from certified suppliers and verifying their gluten content through testing.
Next, the manufacturing facility must be evaluated to prevent cross-contamination. This includes implementing strict cleaning protocols, dedicated equipment, and employee training. Once these steps are completed, the product undergoes laboratory testing to confirm its gluten-free status. Finally, the manufacturer submits the results and documentation to the certifying organization for review and approval.
Choosing the Right Certification Body
Selecting the appropriate certification body is a critical step in the gluten-free certification process. Different organizations have varying standards, fees, and recognition levels. For example, the GFCO requires products to contain less than 10 ppm of gluten, while other organizations may allow up to 20 ppm. Manufacturers should research each certifying body to determine which aligns best with their product and target audience.
It’s also important to consider the organization’s reputation and market recognition. A well-known certification label can enhance a product’s credibility and appeal to consumers. Additionally, manufacturers should evaluate the support and resources provided by the certifying body, such as access to educational materials or marketing tools.
Maintaining Gluten-Free Certification
Once a product is certified gluten-free, maintaining that certification requires ongoing effort. Regular testing and audits are necessary to ensure continued compliance with gluten-free standards. Manufacturers must also stay updated on any changes to certification requirements or industry regulations.
Communication with the certifying body is essential throughout this process. Any modifications to ingredients, suppliers, or manufacturing practices should be reported and reviewed to prevent potential issues. By maintaining a proactive approach, manufacturers can uphold their certification and continue to provide safe, high-quality products to their customers.
The Impact of Gluten-Free Certification on the Market
Gluten-free certification has significantly influenced the food industry, driving innovation and expanding product offerings. As consumer demand for gluten-free options continues to rise, manufacturers are increasingly seeking certification to meet this need. This trend has led to the development of new gluten-free products and improved accessibility for individuals with dietary restrictions.
Certification has also raised awareness about gluten-related health issues, encouraging more people to adopt gluten-free lifestyles. For manufacturers, certification represents an opportunity to tap into a lucrative market while promoting inclusivity and health-conscious choices. The growing prevalence of gluten-free labels reflects a broader shift toward transparency and consumer empowerment in the food industry.







